A Note of X where X = AWS EC2 services.
By Anak Wannaphaschaiyong
An EC2 instance has 4 state of life cycle: running, stopped, and terminated. Furthermore, state transition (or action) of an EC2 instance is launch, rebooting, pending, shutting-down, and stopping, see <ec2_life_cycle>.
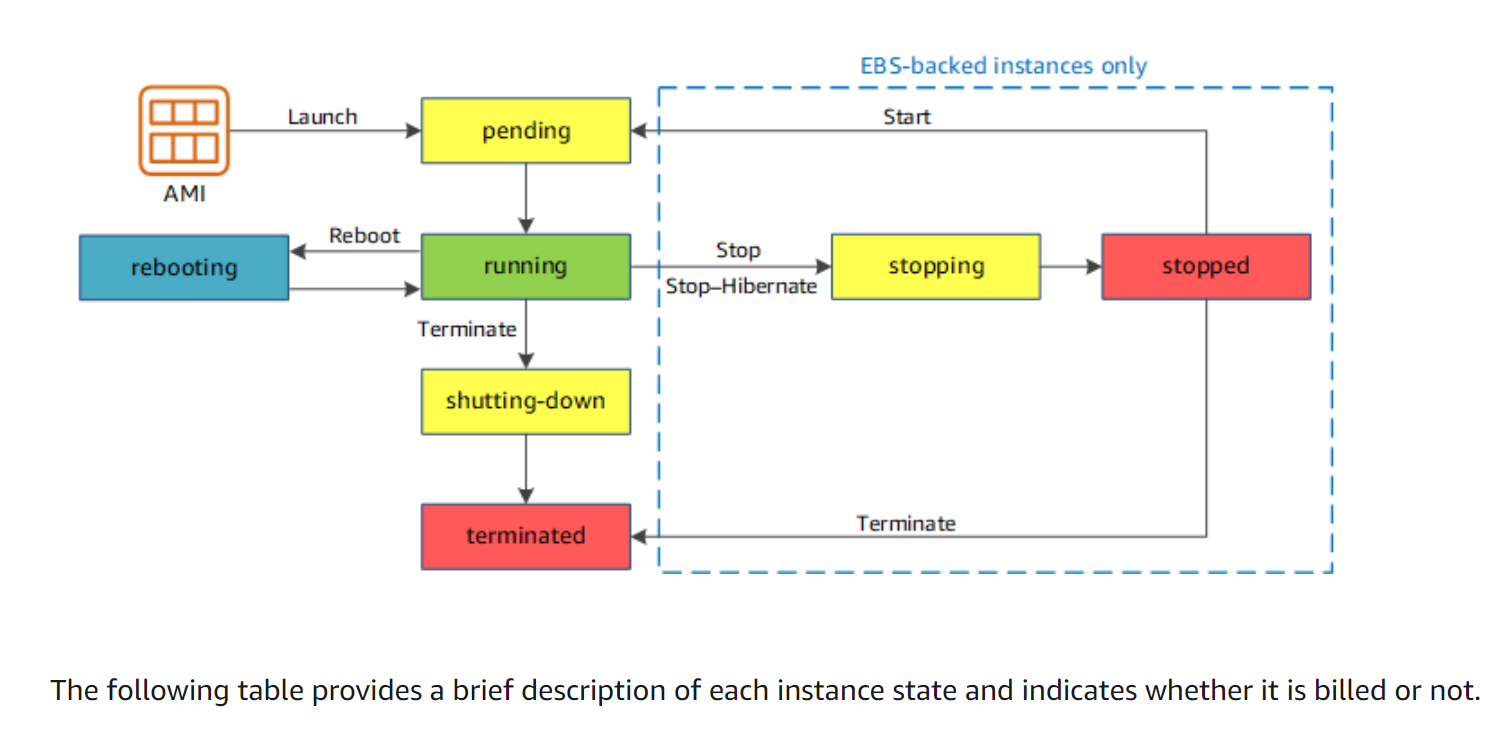
Figure 1: EC2 instance life cycle
Validating that you have correct setup
This article assumes that you have setup AWS credentials in your terminal environment. You can check out one of my article named “Setup AWS credentials for your AWS account and create new user” to help you set things up.
Setup and launch EC2 instance
To launch an EC2 instance, you need to deal with securities 1. Securities part that we need to deal with is authentication and permission. First, you need to authenticate that you have “key” to access an instance. If you don’t already have keypair, you can create keypair as followed:
aws ec2 create-key-pair --key-name <your-key-name> --output text > <your-key-name>.pem
Note that .pem stands for permission. Make sure to save primary key somewhere. You will need to pass .pem to EC2 instance you wish to interact with.
Secondly, you need to obtain AWS IAM policies that allow you to interact with an instance. If you don’t already have IAM users group. You can create one as followed.
aws ec2 create-security-group --group-name <group-name> --description <description>
Using above command, you need assign IAM policies to IAM user group. Note that I haven’t tested the above command manually because I already have IAM users group with appropriate policies. As of [2022-07-11 Mon], I haven’t tried adding policies to IAM identity such as IAM user gruop via command line. I have only tried doing in on AWS console.
To launch EC2 from command line, type in
aws ec2 run-instances --image-id ami-0fb653ca2d3203ac1 --instance-type t2.micro --count 1 --security-group-ids sg-0db2887fa3dbd0493 --key-name <key-name>
Note that permission to access EC2 instance via ssh is separated from permission to access EC2 instance on the browser. Make sure you get the right permission for this.
-
When one interacts with remote services, securities will and must always be taken into account. This may seem unnecessary at times, but, without secure service, existence of a service cannot be justified. ↩︎